Numpy
Table of Contents
1 Numpy
Numpy 是 Python 科学计算的基础包,主要有以下一些功能:
- N 维数组
- 线性代数,傅里叶变换等
import numpy as np
2 基本用法
Numpy 的数组类是 ndarray ,它的别名是 array 。主要 numpy.array 和 Python
自带的 array.array 是不同的。
| 属性 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| arr.ndim | 维度 |
| arr.shape | 每个维度的大小 |
| arr.size | 数组的所有元素个数 |
| arr.dtype | 元素的数据类型 |
| arr.itemsize | 每个元素的字节数 |
| arr.data | 实际数据的引用 |
a0 = np.arange(24).reshape((2, 3, 4)) print(a0) print(a0.ndim) print(a0.shape) print(a0.size) print(a0.dtype) print(a0.itemsize) print(a0.data)
[[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11]] [[12 13 14 15] [16 17 18 19] [20 21 22 23]]] 3 (2, 3, 4) 24 int32 4 <memory at 0x0000021786B458B8>
Numpy 数组和普通数组的区别如下
a0 = [1, 2, 3] print(a0) print(type(a0)) b0 = np.array([6, 7, 8]) print(b0) print(type(b0))
[1, 2, 3] <class 'list'> [6 7 8] <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
3 创建数组
a1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) a2 = np.array([(1.5, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6)]) a3 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=complex) print(a1) print(a2) print(a3)
[1 2 3 4] [[1.5 2. 3. ] [4. 5. 6. ]] [[1.+0.j 2.+0.j] [3.+0.j 4.+0.j]]
4 初始化数组
Numpy 初始化数组一般是生成一定维度的列表,具体如下
np.zeros((3, 4)) np.ones((2, 3, 4), dtype=np.int16) np.empty((2, 3)) np.arange(10, 30, 5) # samillar to range() np.arange(1, 2, 0.3) # but accept float from numpy import pi np.linspace(0, 2, 9) x = np.linspace(0, 2 * pi, 10) y = np.sin(x) print(list(zip(x, y)))
[(0.0, 0.0), (0.6981317007977318, 0.6427876096865393), (1.3962634015954636, 0.984807753012208), (2.0943951023931953, 0.8660254037844387), (2.792526803190927, 0.3420201433256689), (3.490658503988659, -0.34202014332566866), (4.1887902047863905, -0.8660254037844385), (4.886921905584122, -0.9848077530122081), (5.585053606381854, -0.6427876096865396), (6.283185307179586, -2.4492935982947064e-16)]
随机生成数组,获取一些统计信息
a0 = np.random.random((2, 3)) print(a0) print(a0.min(), a0.max()) print(a0.sum()) print(a0.mean()) a1 = np.random.normal(0, 0.1, 10) # mu, sigma, count print(a1[a1 > 0]) print(a1.mean())
[[0.9252851 0.7129627 0.40223125] [0.90696639 0.43173784 0.03253335]] 0.0325333525900483 0.9252851004000952 3.4117166388143234 0.5686194398023873 [0.11057307 0.07345595 0.06929216 0.13555647] -0.03848054532856991
可以通过 Reshape 快速地修改 Python 数组的维度,这个方法非常有用
a1 = np.arange(12) print(a1) a2 = a1.reshape(4, 3) print(a2) print(a2.shape)
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11] [[ 0 1 2] [ 3 4 5] [ 6 7 8] [ 9 10 11]] (4, 3)
当给出数组的维度为 -1 时,代表需要自推导维度大小
a0 = np.arange(30) a0.shape = 2, -1, 3 # -1 means "whatever is needed" print(a0.shape) a1 = a0.reshape(-1, 10) print(a1.shape)
(2, 5, 3) (3, 10)
5 拼接数组
可以使用 vstack 或者 hstack 来拼接数组,不过这样的效率比较低,一般建议直接初始 化对应大小的数组,然后使用 reshape
a1 = np.arange(4).reshape((2, -1)) a2 = a1 + 20 a3 = np.vstack((a1, a2)) print(a3) a4 = np.hstack((a1, a2)) print(a4)
[[ 0 1] [ 2 3] [20 21] [22 23]] [[ 0 1 20 21] [ 2 3 22 23]]
6 基本运算和矩阵相关算法
Numpy 重载了 Python 的数学操作符,基本操作如下
a = np.array([20, 30, 40, 50]) b = np.arange(4) c = a - b print(b**2) # power 10 * np.sin(a) print(a < 35)
[0 1 4 9] [ True True False False]
矩阵的乘法和矩阵里面每个元素相乘
A = np.array([[1,1], [0,1]] ) B = np.array([[2,0], [3,4]] ) print(A * B) # elementwise product print(A @ B) # matrix product print(A.dot(B)) # another matrix product
[[2 0] [0 4]] [[5 4] [3 4]] [[5 4] [3 4]]
基本线性代数的操作
a0 = np.array([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]]) a1 = a0.T # same as a0.transpose() print(a1) a2 = np.linalg.inv(a0) print(a2) I = np.eye(2) J = np.array([[0.0, -1.0], [1.0, 0.0]]) J2 = J @ J # matrix product T0 = np.trace(I) # trace y = np.array([[5.], [7.]]) res1 = np.linalg.solve(a0, y) print(res1) res2 = np.linalg.eig(j) print(res2)
[[1. 3.]
[2. 4.]]
[[-2. 1. ]
[ 1.5 -0.5]]
[[-3.]
[ 4.]]
(array([0.69722436, 4.30277564]), array([[-0.60889368, -0.3983218 ],
[ 0.79325185, -0.91724574]]))
7 深度复制 copy 方法
a0 = np.arange(6) b0 = a0.copy() # a new array object with new data is created print(b0)
[0 1 2 3 4 5]
8 索引
Numpy 的索引是一个比较有用的操作,可以实现快速操作,防止进行使用速度比较慢的 for 循环,同时也可以使代码读起来比较简洁
8.1 使用 Indices 索引
a0 = np.arange(12)**2 # the first 12 square numbers print(a0) print(a[2]) # the elements of a at the positions i b0 = np.array([1, 1, 3, 8, 5]) # an array of indices print(a0[b0]) # get elements with indices as b0
[ 0 1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81 100 121] 40 [ 1 1 9 64 25]
在实际工程可以使用下标索引来掩码 (mask),挑选出对应的色块
palette = np.array([ [0, 0, 0], # black [255, 0, 0], # red [0, 255, 0], # green [0, 0, 255], # blue [255, 255, 255] # white ]) image = np.array([ [0, 1, 2, 0], # each value corresponds to a color in the palette [0, 3, 4, 0] ]) res = palette[image] # the (2,4,3) color image print(res)
[[[ 0 0 0] [255 0 0] [ 0 255 0] [ 0 0 0]] [[ 0 0 0] [ 0 0 255] [255 255 255] [ 0 0 0]]]
a0 = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4) i = np.array([[0, 1], [1, 2]]) # indices for the first dim of a j = np.array([[2, 1], [3, 3]]) # indices for the second dim print(a0) a1 = a0[i, j] # i and j must have equal shape print(a1) b1 = a0[i, 2] print(b1) b2 = a0[:, j] # i.e., a[ : , j] print(b2)
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11]] [[ 2 5] [ 7 11]] [[ 2 6] [ 6 10]] [[[ 2 1] [ 3 3]] [[ 6 5] [ 7 7]] [[10 9] [11 11]]]
8.2 使用布尔值索引
Numpy 支持使用条件
a0 = np.arange(6).reshape(3, 2) b0 = a0 > 4 print(b0) print(a0[b0]) # 1d array with the selected elements a0[b0] = 0 # All elements of 'a' higher than 4 become 0 print(a0)
[[False False] [False False] [False True]] [5] [[0 1] [2 3] [4 0]]
多维度的索引
a0 = np.arange(10).reshape(2, -1) print(a0) b1 = np.array([False, True]) # first dim selection b2 = np.array([True, False, True, False, False]) # second dim selection print(a0[b1, :]) # selecting rows a0[b1] # same thing a0[:, b2] # selecting columns print(a0[b1, b2]) # a weird thing to do
[[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9]] [[5 6 7 8 9]] [5 7]
9 借助 matplotlib 画一些统计图
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt filename = '../static/image/2018/10/numpy1.png' # Build a vector of 10000 normal deviates with variance 0.5^2 and mean 2 mu, sigma = 2, 0.5 v = np.random.normal(mu,sigma,10000) # Plot a normalized histogram with 50 bins plt.hist(v, bins=50, density=1) # matplotlib version (plot) plt.savefig(filename) return filename
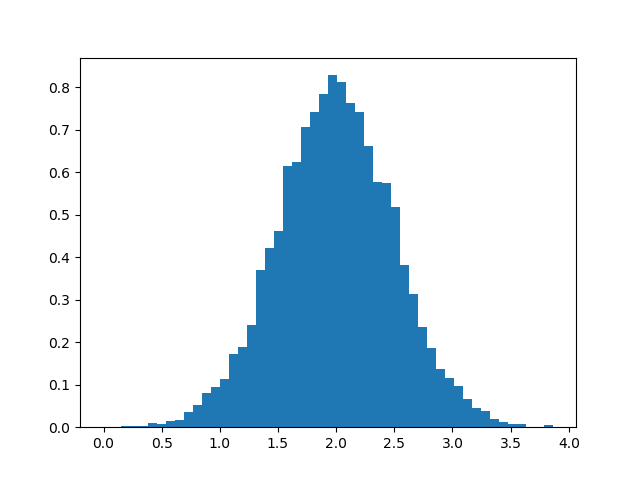
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt filename = '../static/image/2018/10/numpy2.png' # Build a vector of 10000 normal deviates with variance 0.5^2 and mean 2 mu, sigma = 2, 0.5 v = np.random.normal(mu,sigma,10000) # Compute the histogram with numpy and then plot it (n, bins) = np.histogram(v, bins=50, density=True) # NumPy version (no plot) plt.plot(.5*(bins[1:]+bins[:-1]), n) plt.savefig(filename) return filename
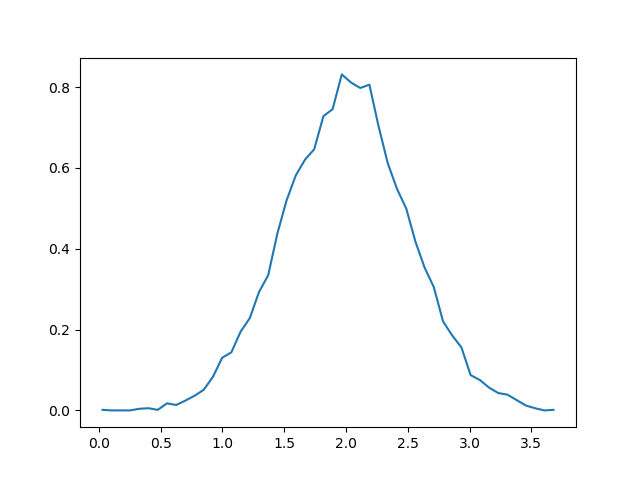
10 安装 Numpy 和测试
使用 pip 安装
pip install numpy
运行 Numpy 自带的测试
python -c "import numpy; numpy.test()"