PostgreSQL 关系数据库
Table of Contents
1 PostgreSQL
1.1 简介
PostgreSQL 是一种特性非常齐全的自由软件的对象-关系型数据库管理系统(ORDBMS), 是以加州大学计算机系开发的 POSTGRES,4.2 版本为基础的对象关系型数据库管理系统。 POSTGRES 的许多领先概念只是在比较迟的时候才出现在商业网站数据库中。PostgreSQL 支持大部分的 SQL 标准并且提供了很多其他现代特性,如复杂查询、外键、触发器、视 图、事务完整性、多版本并发控制等。同样,PostgreSQL 也可以用许多方法扩展,例如 通过增加新的数据类型、函数、操作符、聚集函数、索引方法、过程语言等。另外,因 为许可证的灵活,任何人都可以以任何目的免费使用、修改和分发 PostgreSQL
1.2 Windows
首先去官网上下载所需的安装文件
我下载的是 postgresql-9.6.11-1-windows-x64.exe ,双击点开是直接报错安装不了,
出现如下提示:
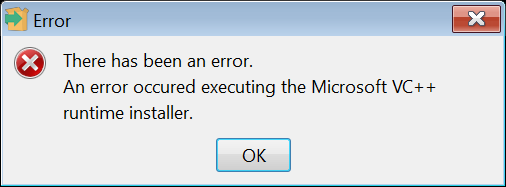
通过网络资料查找得知,可以通过跳过本地 C++ 运行库来解决这个错误。具体安装使用 如下命令行。
postgresql-9.6.11-1-windows-x64.exe --install_runtimes 0
1.3 MacOS
1.3.1 使用 Homebrow 安装
这里安装 9.6 版本的 postgres
brew install postgresql@9.6
Homebrew 安装过后的数据库不包含任何信息,需要初始化数据库基本信息文件
initdb /usr/local/var/postgresql@9.6 -E UTF8
1.3.2 初始创建数据库和账户
createdb
1.3.3 配置允许远程连接数据库
postgres 默认只能通过 localhost 连接,如果需要建立远程连接则需要进行配置。找
到 postgres 配置文件所在目录,homebrew 安装后默认配置文件位于
/usr/local/var/postgresql@9.6
修改 postgresql.conf: 配置监听任意 IP
listen_addresses = '*'
修改 pg_hba.conf: 配置服务端允许 MD5 认证方式,即使用用户名和密码登录
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
修改过后需要重启才能生效
2 psql 命令行工具
2.1 登录数据库
直接将密码放到命令行中安全性低,可以被其它用户通过 ps 命令看到。PostgreSQL
建议将密码统一存放在本地文件中,文件的路径如下:
- Mac & Linux:
~/.pgpass - Windows:
%APPDATA%\postgresql\pgpass.conf
Unix 操作系统上还需要需要设置密码文件的访问权限
touch ~/.pgpass chmod 0600 ~/.pgpass
密码文件的格式如下:
hostname:port:database:username:password
- 使用
#可以注释 - 前四个字段可以是
*,表示匹配任何数据项
psql -U user -d database -h hostname
2.2 Ubuntu 下登录数据库
Ubuntu 操作系统中默认可以通过 postgres 用户直接进入数据库
sudo -u postgres psql
2.3 常见控制台命令
\password:设置当前登录用户的密码 \h:查看 SQL 命令的解释,比如\h select。 \?:查看 psql 命令列表。 \l:列出所有数据库。 \c [database_name]:连接其他数据库。 \d:列出当前数据库的所有表格。 \d [table_name]:列出某一张表格的结构。 \du:列出所有用户。 \e:打开文本编辑器。 \conninfo:列出当前数据库和连接的信息。 \password [user]: 修改用户密码 \q:退出
2.4 查看表结构及注释
psql 的可以使用 \d 显示一个表的结构,如果需要显示每行的注释,可以使用 \d+
选项。
pgdb=> \d students;
Table "public.students"
Column | Type | Modifiers
------------+-----------------------------+-------------------------------------------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('global_id'::regclass)
code | character varying(32) |
created_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now()
updated_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now()
name | character varying(64) | not null
gender | character varying(1) |
phone | character varying(16) |
joined_at | date |
Indexes:
"students_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
Referenced by:
TABLE "course_students" CONSTRAINT "course_students_student_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(id)
TABLE "scores" CONSTRAINT "scores_student_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(id)
pgdb=> \d+ students;
Table "public.students"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
------------+-----------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+----------------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('global_id'::regclass) | plain | |
code | character varying(32) | | extended | |
created_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
updated_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
name | character varying(64) | not null | extended | |
gender | character varying(1) | | extended | | M = Male, F = Female
phone | character varying(16) | | extended | |
joined_at | date | | plain | |
Indexes:
"students_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
Referenced by:
TABLE "course_students" CONSTRAINT "course_students_student_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(id)
TABLE "scores" CONSTRAINT "scores_student_id_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(id)
2.5 竖行显示查询结果
有时候查看的行数比较多,不方便一次性浏览,可以使用 \x 来开启竖行显示,这样
结果更加易读。
pgdb=> select * from users; id | code | created_at | updated_at | username | nickname | password | birthday --------+------+----------------------------+----------------------------+-----------+------------+----------+------------ 100001 | | 2019-06-20 20:05:56.214153 | 2019-06-20 20:05:56.214153 | admin | SuperUser | | 100000 | | 2019-06-20 20:05:56.116695 | 2019-06-22 22:21:48.667 | hujinghui | Jinghui Hu | | 1992-06-15 (2 rows) pgdb=> \x Expanded display is on. pgdb=> select * from users; -[ RECORD 1 ]-------------------------- id | 100001 code | created_at | 2019-06-20 20:05:56.214153 updated_at | 2019-06-20 20:05:56.214153 username | admin nickname | SuperUser password | birthday | -[ RECORD 2 ]-------------------------- id | 100000 code | created_at | 2019-06-20 20:05:56.116695 updated_at | 2019-06-22 22:21:48.667 username | hujinghui nickname | Jinghui Hu password | birthday | 1992-06-15
3 数据库和表操作
3.1 查看数据库基本信息
-- 查看所有数据库列表 \l -- 查看当前数据库 select current_database();
3.2 数据库操作命令
-- 连接数据库 \c <database_name> -- 创建数据库 create database <database_name> with owner <username>; -- 删除数据库 drop database if exists <database_name>; -- 重命名数据库 alter database <old_name> rename to <new_name>;
3.3 创建用户及数据库
create database dbname owner username; grant all privileges on database dbname to username;
3.4 查看表基本信息
-- 查看当前数据库的所有表 \dt -- 查看全局的表 \dt *.*
avic=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+-----------------------+----------+-------
public | tb_departments | table | avic
public | tb_departments_id_seq | sequence | avic
public | tb_users | table | avic
public | tb_users_id_seq | sequence | avic
(4 rows)
avic=# \d tb_users
Table "public.tb_users"
Column | Type | Modifiers
---------------+-----------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('tb_users_id_seq'::regclass)
available | boolean | not null default true
created_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now()
updated_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now()
department_id | integer | not null
tag | character varying(64) | not null
name | character varying(64) | not null
info | json |
Indexes:
"tb_users_pk" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
Foreign-key constraints:
"tb_users_department_id_fk" FOREIGN KEY (department_id) REFERENCES tb_departments(id)
avic=# \d+ tb_users
Table "public.tb_users"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
---------------+-----------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('tb_users_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |
available | boolean | not null default true | plain | |
created_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
updated_at | timestamp without time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
department_id | integer | not null | plain | |
tag | character varying(64) | not null | extended | |
name | character varying(64) | not null | extended | | Username
info | json | | extended | |
Indexes:
"tb_users_pk" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
Foreign-key constraints:
"tb_users_department_id_fk" FOREIGN KEY (department_id) REFERENCES tb_departments(id)
avic=#
3.5 创建/删除表
- 记得遵循命名规范, 表名
tb_tabnames, 主键pk_tabnames, 外键fk_tabnames_fieldname serial表创建对应在自增序列,另外还有smallserial和bigserialcreate table tb_products (id serial); -- 相当于创建了一个序列,并将对于字段默认赋值成序列的 nextval create sequence tb_products_id_seq increment by 1 minvalue 1 no maxvalue start with 1; create table tb_products (id default default nextval('tb_products_id_seq'));
JSON 字段也是 pg 默认支持的,pg 中的 JSON 有两种:
json写入快,读取慢jsonb写入慢,读取快
select info from name_age where info @> '{"id":1}'::jsonb; select info -> 'name' from name_age where (info ->> 'age')::int4 > 16;
create table if not exists tb_departments ( id serial not null, available boolean not null default true, created_at timestamp not null default current_timestamp, updated_at timestamp not null default current_timestamp, tag varchar(64) not null, name varchar(64) not null, constraint pk_departments primary key (id) ); drop table if exists tb_users; create table if not exists tb_users ( id serial not null, available boolean not null default true, created_at timestamp not null default current_timestamp, updated_at timestamp not null default current_timestamp, department_id integer not null, tag varchar(64 name varchar(64) not null, info json, constraint pk_users primary key (id), constraint pk_users_department_id foreign key (department_id) references tb_departments (id) ); comment on column tb_users.name is 'Username';
如果表存在的话,删除表
drop table if exists tb_users cascade;
另外,如果需要创建全局数据库的序列,可以参考如下方式
create sequence global_id_seq increment by 1 minvalue 1 no maxvalue start with 9999; create table tb_users ( id int not null default nextval('global_id_seq'), constraint pk_users primary key(id) ); alter table tb_users owner to username;
4 用户/权限
4.1 查看用户基本信息
-- 查看所有用户列表: select rolname from pg_roles; -- 查看当前用户: select current_user; -- 查看当前用户权限 \du
4.2 用户信息相关的操作命令
-- 查看所有用户 select rolname from pg_roles; -- 创建用户 create user username with password 'password'; -- 删除用户 drop user if exists username; -- 修改用户密码 alter role username with password 'password'; alter user postgres with password 'postgres';
5 工作流
5.1 调整表中的列顺序
pg 中建好的表是不能轻易调整顺序的,不过可以通过重命名,导数据的方式曲线救国。 该方法对数据量大表慎用。 改表有风险,建表需谨慎
alter table tabname rename to oldtbl; create table tabname ( -- column defs go here ); insert into tabname (col1, col2, col3) select col1, col2, col3 from oldtblk;
延伸讨论一下,数据库表的作为计算机底层结构,一般不需要人来看懂,在看表时最好 建一个视图来看,视图的优点是可以将一些人看不懂的 ID 直接转换成名称, 不要懒, 要学会用视图来处理此类问题。
5.2 数据备份与还原
pg 提供两个操作命名
# 备份数据库: -s 选项只导出 schema, -O 选项不导出表所属用户信息 pg_dump <database_name> # 还原数据库 pg_restore -d <database_name> -a <file_pathway>
psql 中复制有 \copy 和 copy 两种,其中 \copy 处理的 csv 文件在客户机端,
copy 处理的在服务器端
-- 导出 csv 文件 \copy tablename to 'filepath' csv; -- 导入 csv 文件, Excel 默认识别中文编码是GBK, 可加 encoding 'GBK' 解决编码问题 \copy tablename from 'filepath' csv; -- Excel 默认识别中文编码是GBK, 可加 encoding 'GBK' 解决编码问题 \copy tablename to 'filepath' csv encoding 'GBK';
5.3 导出数据库表
导出多个表可创建如下的文件,然后直接使用命令行执行脚本的方式导出文件
-- dump.sql set client_encoding = 'GBK'; -- Windows 的 Excel 只认 GBK 格式 \copy (select * from vw_products) to '1.基础表.产品表.csv' with csv header; \copy (select u.tag as unit_tag from vm_unit u) to '2.关联表.csv' with csv header;
使用命令执行脚本导出
psql -U user -h host -d database -f dump.sql
5.4 导入本地 CSV 文件的数据库表
整理出 CSV 文件过后,导入一个临时表中
create table imp(c1 varchar, c2 varchar, c3 varchar, c4 varchar); \copy imp(c1, c2, c3) from '/tmp/w.csv' delimiter ',' csv header encoding 'GBK';
在 psql 命令行中使用如下方式导入
database=# create table imp(c1 varchar, c2 varchar, c3 varchar, c4 varchar);
CREATE TABLE
database=# \copy imp(c1, c2, c3) from '/tmp/w.csv' delimiter ',' csv header encoding 'GBK';
COPY 10
database=# select * from imp;
c1 | c2 | c3 | c4
------------+----+----+----
WF0031S002 | 20 | 16 |
WF0031S003 | 16 | 25 |
WF0031S004 | 25 | 2 |
WF0031S005 | 2 | 24 |
WF0031S006 | 24 | 26 |
WF0031S007 | 26 | 27 |
WF0031S008 | 27 | 28 |
WF0031S009 | 28 | 3 |
WF0031S010 | 3 | 32 |
WF0031S011 | 32 | 33 |
(10 rows)
一顿操作过后,再用类似于下面的语句导入目标表
insert into tb_names(id, tag) select c2::integer, c1 from imp;
5.5 使用 pgAdmin4 的 Docker 版本
一些细节参考 pgAdmin4 Docker Manual 中的描述
docker run -d --restart always \ --name pgadmin4 \ -p 5050:80 \ -e 'PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL=pgadmin@example.com' \ -e 'PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD=pgadmin' \ dpage/pgadmin4:4.18
如果使用 Nginx 做反向代理可以参考如下配置
server { listen 80; server_name _; location /pgadmin4/ { proxy_set_header X-Script-Name /pgadmin4; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_pass http://localhost:5050/; proxy_redirect off; } }